
Exploring Significance of ++ Operator in Java Programming
In the world of programming, operators play a crucial role in performing various operations on data. One such operator that often raises questions, especially among beginners, is the “++” operator in Java. The “++” operator, known as the increment operator, holds a significant place in Java’s syntax and programming practices. In this article, we’ll dive deep into understanding what the “++” operator means in Java, how it works, and its various use cases.
Understanding the Increment Operator
In Java, the “++” operator is used to increment the value of a variable by 1. It is often referred to as the “increment operator.” The syntax of the increment operator is simple: it is represented as two plus signs placed immediately after the variable, such as `variable++`. Similarly, the “–” operator represents the decrement operator, which decreases the value of a variable by 1.
The increment operator has both a pre-increment and a post-increment form. In the pre-increment form, the increment operation is performed before the value of the variable is used in an expression. In the post-increment form, the value of the variable is used in an expression before the increment operation takes place.
“`java
int x = 5;
int y = ++x; // Pre-increment
“`
In this example, `x` is incremented first, and then its value is assigned to `y`. After this code, both `x` and `y` will have the value 6.
“`java
int a = 5;
int b = a++; // Post-increment
“`
Here, the value of `a` (5) is assigned to `b` first, and then `a` is incremented. After this code, `a` will have the value 6, while `b` will have the value 5.
Some examples
The increment operator, denoted as ++, serves to raise the value of a variable by 1. Its function can be employed either as a pre-increment or post-increment operator.
When used as a pre-increment, the ++ operator is positioned before the variable. For instance, if we have a variable i, the expression ++i signifies a pre-increment operation. This means that the value of i is incremented prior to being utilized in any operations involving i.
To illustrate, consider the variable i. In the operation ++i, the value of i is elevated by 1, effectively performing the same action as i = i + 1. This modification occurs before the new value of i is utilized in any subsequent operations.

The utilization of pre-increment operators is applicable for the purpose of increasing numeric data types. In the case of the integer data type, pre-increment serves as a method to raise the value of the integer by 1. An illustrative program is available to showcase the practical implementation of the increment operator.
The output is:
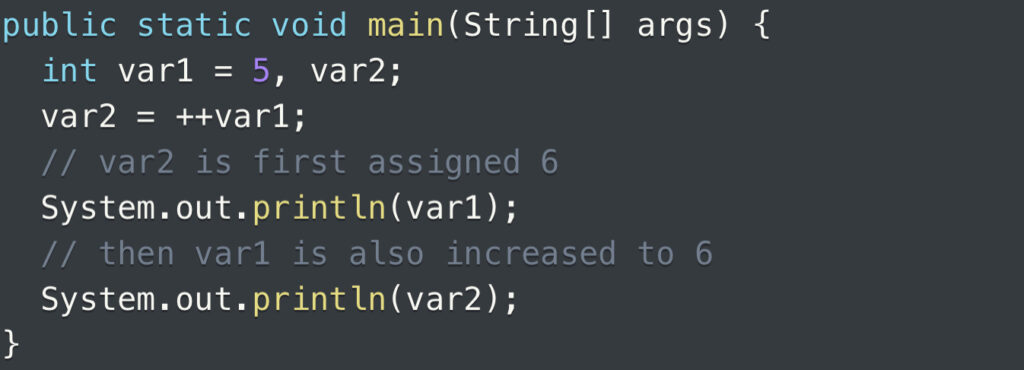
6
6
When dealing with the float data type, it’s possible to employ the pre-increment operator to elevate the value of a float variable by 1 unit. A provided example program below serves to demonstrate this concept.
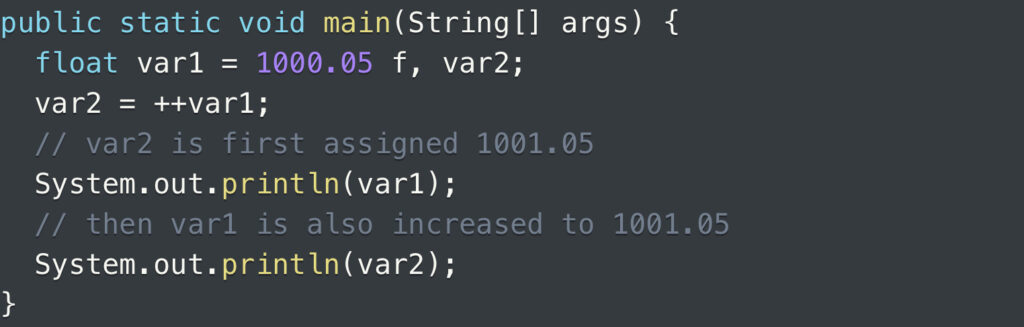
The output is:
1001.05
1001.05
When considering the double data type, one can utilize the pre-increment operator to enhance the value of a double variable by 1. An accompanying example further elucidates the practical application of the increment operator in this context.
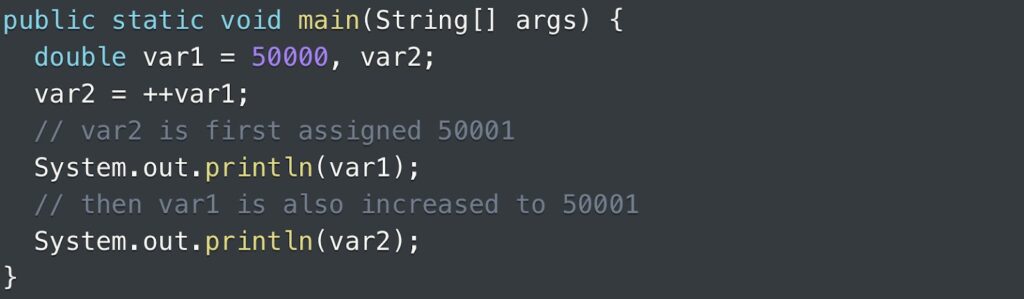
Output:
50001.0
50001.0
The short data type enables the utilization of a pre-increment operator to raise the value of a short variable. An example is presented below to provide a clear demonstration of how the increment operator can be employed in this scenario.
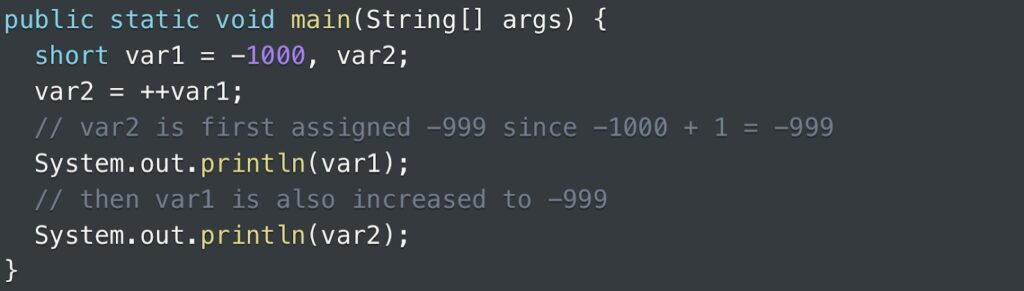
Output is:
-999
-999
In the case of the long data type, employing the pre-increment operator permits the enhancement of a long variable’s value by 1. An illustrative example provided below serves to showcase the practical implementation of the pre-increment operation specifically for the long data type.

Output:
2541
2541
When dealing with the double data type, the post-increment operator proves useful for increasing the value of a variable by 1. An example is provided below to demonstrate the application of the post-increment operator specifically for double data types.
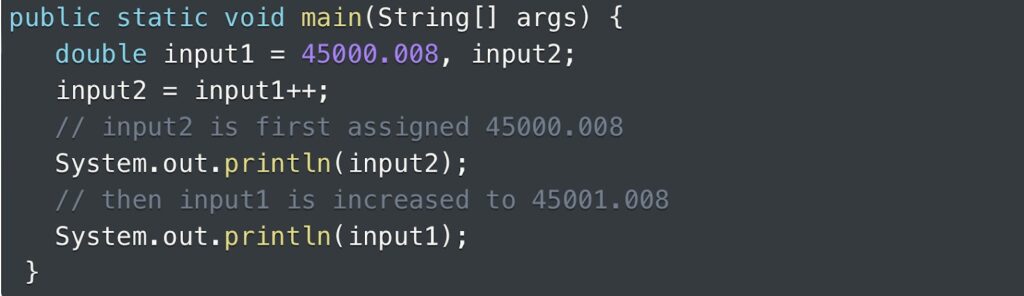
The output is:
45000.008
45001.008
When addressing the byte data type, one can employ the post-increment operator to raise the value of a variable by 1.
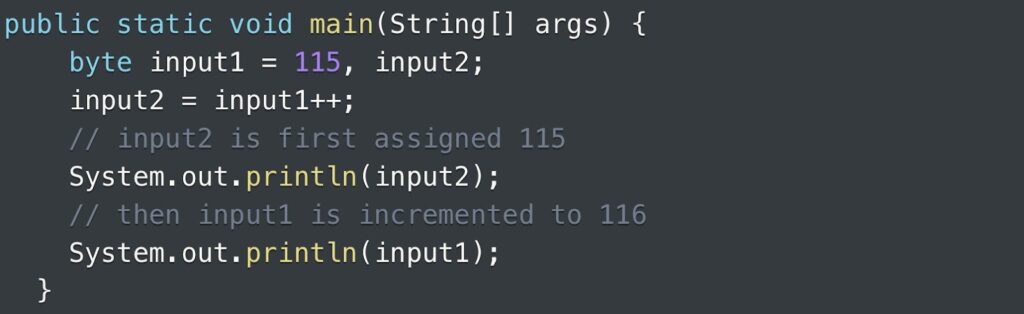
The output is:
115
116
Use Cases of the Increment Operator
The increment operator has various use cases in Java programming, making it an essential tool in a developer’s toolbox. Let’s explore some of these use cases:
1. Looping Constructs
One of the most common uses of the increment operator is in looping constructs such as the `for` loop. It allows developers to iterate over a range of values and perform operations within the loop body.
“`java
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(“Iteration: ” + i);
}
“`
In this example, the increment operator is used to increase the value of `i` in each iteration of the loop.
2. Array Traversal
When working with arrays, the increment operator can be employed to traverse through the elements of an array.
“`java
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
System.out.println(“Element: ” + numbers[i]);
}
“`
Here, the increment operator helps in accessing each element of the array sequentially.
3. Counter Variables
Incrementing variables are often used as counters to keep track of occurrences or operations.
“`java
int clickCount = 0;
// Code for handling user clicks
clickCount++;
“`
In this scenario, the variable `clickCount` is incremented to track the number of user clicks.
4. Numeric Calculations
The increment operator can be utilized in various numeric calculations.
“`java
int total = 0;
total += 5; // Increment by 5
“`
Here, the increment operator is indirectly used to increase the value of `total` by 5.
5. Implementing Algorithms
Certain algorithms and logic require the use of increment operators to achieve their intended functionality.
“`java
int factorial = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
factorial = i;
}
“`
In this factorial calculation, the increment operator assists in iterating through the numbers from 1 to `n`.
Precautions and Pitfalls
While the increment operator is a valuable tool for manipulating variables, its usage must be approached with caution to prevent unintended behavior and potential bugs in your code.
1. Side Effects
Incorporating the increment operator into intricate expressions can yield side effects that complicate code comprehension. For instance:
“`java
int result = a++ + ++b;
“`
The result of `result` may be difficult to predict due to the combination of pre-increment and post-increment operators.
2. Infinite Loops
Misusing the increment operator in loop conditions can lead to infinite loops, as demonstrated in this example:
“`java
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i–) {
// Code
}
“`
Here, the loop persists indefinitely because the value of `i` never approaches 5.
3. Precision Loss
When handling floating-point numbers, the increment operator might result in precision loss:
“`java
double value = 0.1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
value += 0.1;
}
“`
Due to the inherent nature of floating-point representation in computers, calculations involving decimal values might not always yield perfectly accurate results. This can have implications when using the increment operator on floating-point variables.
In the given example:
“`java
double value = 0.1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
value += 0.1;
}
“`
The initial value of `0.1` might not be represented exactly in binary floating-point, leading to tiny inaccuracies with each iteration. Consequently, the final value of `value` may not exactly equal `1.0`, even though the loop iterated 10 times. This phenomenon is a consequence of how floating-point numbers are stored and processed in binary form. To mitigate this issue, developers often resort to methods like rounding or using special libraries designed for precise decimal calculations when handling monetary values or other situations requiring high precision.
Conclusion
The “++” operator, also known as the increment operator, holds a significant role within Java programming due to its versatility in tasks such as loop management and mathematical computations. It is crucial to grasp both its pre-increment and post-increment variations to optimize coding practices.
- In its pre-increment form (++x), the value is increased before its use in an expression. This can be beneficial when ensuring the updated value is employed immediately. On the other hand, the post-increment form (x++) raises the value after its use in an expression, which can be advantageous in specific scenarios;
- Utilizing the increment operator can expedite iterative processes, like incrementing loop variables. However, its usage within complex expressions requires caution to avoid unexpected outcomes and side effects. The operator’s behavior can differ when combined with other operators, leading to unforeseen results.
Proficient understanding of the increment operator empowers developers to craft efficient and reliable Java applications. By choosing the appropriate form and implementing it judiciously, programmers can bolster their coding skills and produce robust software solutions. In summary, mastering the nuances of the increment operator is pivotal for enhancing code quality and optimizing the development process.
