
Master The Art Of Integrating Liquibase With Spring Boot
In the world of modern software development, the synergy between various technologies is pivotal for delivering high-quality applications. One such integration that significantly enhances database management within Spring Boot projects is the incorporation of Liquibase. This article takes you through a step-by-step journey of adding Liquibase to your Spring Boot application, enriching your understanding with real-world examples and best practices.
Introduction to Liquibase and Spring Boot
Liquibase and Spring Boot are two essential tools that, when combined, facilitate seamless database version control and management within your Java applications. By utilizing Liquibase, developers can ensure a consistent database schema while minimizing the risk of errors during updates.
Why Combine Liquibase with Spring Boot?
Integrating Liquibase with Spring Boot provides numerous benefits, including:
- Version Control: Maintain a structured record of database schema changes;
- Collaboration: Enable teams to collaborate effectively on database modifications;
- Automated Updates: Automate the application of database changes during deployment;
- Rollback Capability: Effortlessly roll back changes in case of issues.
Setting Up Your Spring Boot Project
To get started, let’s set up a basic Spring Boot application:
- Create a New Spring Boot Project: Use Spring Initializr to generate a new project with necessary dependencies;
- Configure Database Properties: Configure your application’s application.properties or application.yml file to provide database connection details.
Integrating Liquibase
Now comes the exciting part—integrating Liquibase into your Spring Boot project!
Step 1: Add Dependencies
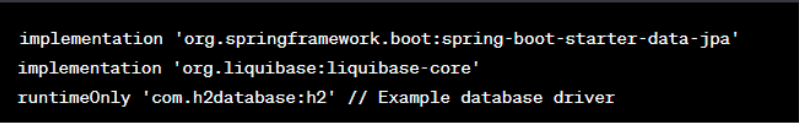
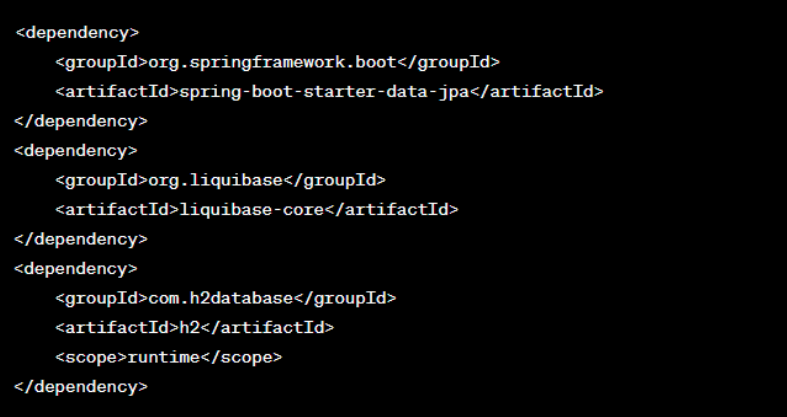
In your build.gradle or pom.xml, add the Liquibase and database driver dependencies.
For Gradle:
For Maven:
Step 2: Create Change Logs
Liquibase operates through change logs—XML, YAML, or SQL files that define database changes.
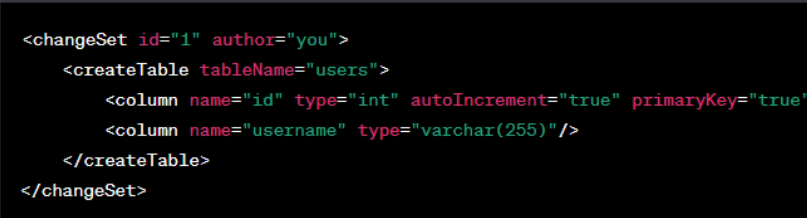
- Create a Change Log File: Add a new file named changelog.xml under src/main/resources/db/changelog/;
- Define Changes: Within the change log, use Liquibase’s syntax to define changes like creating tables, adding columns, and more.
Example:
Step 3: Apply Changes
Liquibase automatically applies changes during application startup. Run your Spring Boot application, and Liquibase will execute the defined changes against the configured database.
Best Practices and Tips
- Use Descriptive Change Set IDs: Make your change set IDs meaningful for easier tracking;
- Group Related Changes: Group changes in a single change set for improved organization;
- Leverage Pre-Conditions: Use pre-conditions to ensure specific conditions before applying changes.
Comparison Table: Liquibase vs. Manual Scripting
| Aspect | Liquibase | Manual Scripting |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Moderate | High |
| Version Tracking | Built-in | Manual |
| Collaboration | Easier with version control systems | Prone to errors without proper coordination |
| Rollback Support | Yes | Manual |
Code Snippet: Applying Rollback
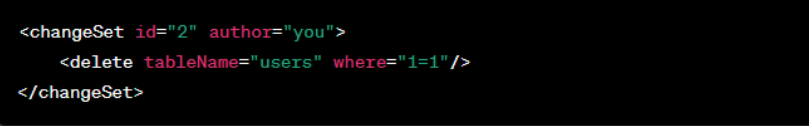
In your change log, define rollback commands alongside the main change.
Example:
Handling Data Migrations
Migrating data alongside schema changes is a common requirement. Liquibase supports data migration through change sets, enabling you to insert, update, or delete data as needed.
Adding Data Change Set
- Create a Data Change Set: Within your change log, add a new change set for data migration;
- Define Data Changes: Utilize Liquibase’s commands to insert, update, or delete data rows.
Example:
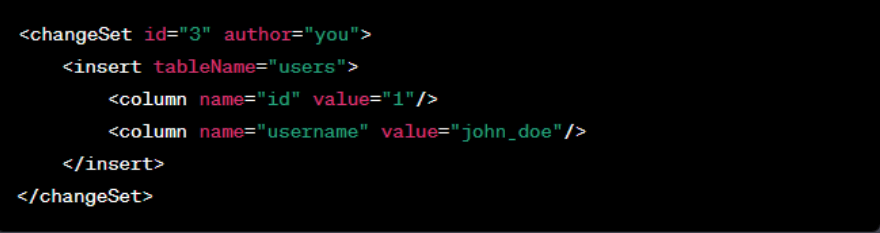
Executing Data Changes
When you run your Spring Boot application, Liquibase will apply both schema changes and data migrations in a seamless manner.
Advanced Features and Customization
Liquibase offers advanced features to handle complex scenarios and customization requirements.
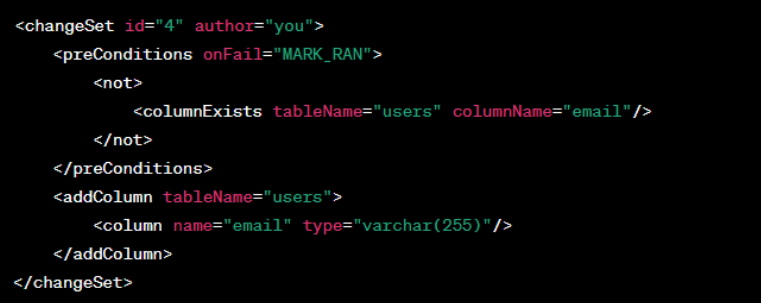
Conditional Changes
Apply changes based on conditions using Liquibase’s <preConditions> tag.
Example:
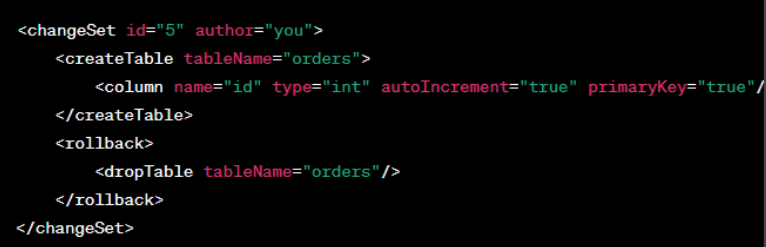
Rollback and Rollback Tags
Define <rollback> sections within change sets to handle rollback operations. Utilize rollback tags for point-in-time recovery.
Example:
Integrating Liquibase with Continuous Integration
Maintaining database changes along with code changes is crucial for consistent deployments. Integrating Liquibase with your CI/CD pipeline ensures that changes are applied automatically.
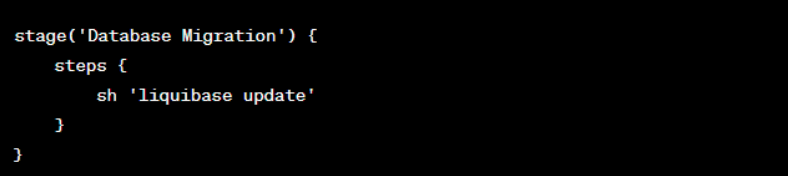
CI/CD Integration Steps
- Configure CI/CD Workflow: Integrate Liquibase commands into your CI/CD pipeline;
- Run Liquibase Commands: Execute Liquibase commands during the deployment process.
Example (using Jenkins Pipeline):
Monitoring and Managing Liquibase Changes
As your application evolves, keeping track of database changes becomes paramount. Liquibase provides tools for monitoring and managing these changes.
Liquibase Diff
Use Liquibase’s diff commands to generate a changelog from the difference between two database schemas.
Example:

Liquibase UpdateSQL
Generate SQL scripts for planned changes without applying them. This allows you to review changes before execution.
Example:

Handling Complex Schema Changes
As applications evolve, so do their database schemas. Liquibase excels at managing complex schema changes without disrupting your application’s functionality.
Renaming Columns and Tables
Liquibase allows you to rename columns and tables while retaining data and relationships.
Splitting and Merging Tables
When data needs to be divided among multiple tables or consolidated into one, Liquibase simplifies the process.
Changing Data Types
Easily change data types of columns while preserving existing data, ensuring seamless transitions.
Versioning and Collaboration
Version control and collaboration are crucial in software development. Liquibase facilitates effective collaboration among developers working on the same project.
Versioned Change Logs
Liquibase generates versioned change logs, enabling developers to track and manage changes systematically.
Collaboration with VCS
Integrate Liquibase with version control systems like Git to keep track of schema changes.
Handling Merge Conflicts
Liquibase’s versioned change logs mitigate merge conflicts, ensuring a smooth collaboration process.
Liquibase Extensions and Plugins
Liquibase’s extensibility allows you to enhance its capabilities with various extensions and plugins.
Database-Specific Extensions
Leverage database-specific extensions for added functionalities tailored to your database engine.
Custom Change Types
Develop custom change types to implement specialized changes not covered by default Liquibase commands.
Reporting Plugins
Use reporting plugins to generate comprehensive reports detailing your database changes.
Handling Rollbacks with Liquibase
Rollbacks are essential for recovering from unexpected issues during deployment. Liquibase provides a structured approach to handling rollbacks.
Automatic Rollbacks
Liquibase’s automatic rollback feature ensures that if any change set fails during execution, previous changes are automatically rolled back.
Manual Rollbacks
In cases where automatic rollbacks aren’t sufficient, Liquibase enables manual rollbacks through the rollback command.
Point-in-Time Recovery
Liquibase allows you to specify a point in time to which you want to roll back, ensuring precise recovery.
Alt: Reliable Database Migrations with Liquibase, Video
Managing Database Environments
In real-world applications, you often need to manage multiple environments, each with its own database configurations. Liquibase simplifies this process.
Environment-Specific Configuration
Customize your Liquibase configuration for different environments, adjusting database connections and settings.
Database Migration Scripts
Generate migration scripts for different environments to ensure consistent changes across development, staging, and production.
Version Control for Environments
Keep track of changes made to each environment’s database schema, maintaining version control throughout.
Conclusion
Integrating Liquibase into your Spring Boot projects empowers you to manage database schema changes with precision and ease. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can streamline your development process and ensure a robust database management strategy.
FAQs
Yes, Liquibase can be integrated with various Java projects, not limited to Spring.
Absolutely! Liquibase supports a wide range of database systems, providing flexibility.
Yes, Liquibase allows you to define rollback operations for each change set.
No, you can also use XML and YAML formats to define changes in Liquibase.
Yes, you can configure Liquibase to apply changes during integration tests.
